A chief technology officer is the head of an organization’s technology strategy, overseeing its IT and data management. They are responsible for devising technical strategies to enhance business operations, leading technology teams, and collaborating with stakeholders to drive innovation and improve customer experience. Furthermore, the modern CTO plays a crucial role in promoting a “security-by-design” approach, where security considerations are integrated from the beginning of product development–a concept known as “shift-left security.”
As advancements in IT are rampant due to the impact of technologies such as AI, the need for technology personnel in leadership positions is estimated to increase by 17% by 2033 (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2024). This is possibly due to the need for leadership skills to innovate, plan, and manage technology capabilities augmented by AI and ML. A ZipRecruiter search in January 2025 showed approximately 44,000 vacancies for the CTO across the globe, with an average salary of $166,511 per annum (ZipRecruiter, 2025).
Studies have suggested that by 2026, over 90% of organizations globally will face challenges due to IT skill shortages (IDC, 2024). Hence, this indicates that the corporate landscape is experiencing a significant surge in demand for skilled technology leaders driven by rapid advancements.
The growing demand for skilled technology leaders calls for organizations to implement proactive strategies to attract, nurture, and retain top talent. Addressing these challenges allows organizations to develop a skilled workforce that will advance their tech capabilities and sustain a competitive edge.
The Roles and Responsibilities of a Chief Technology Officer
The role of a CTO is both pivotal and multifaceted, encompassing the management of hardware, software, data, and networks, as well as the development of technology solutions for clients. The skills needed for effectively executing these roles, including technical, managerial, and interpersonal, are also equally important (LinkedIn, n.d.).
Key Accountabilities of a CTO
On a regular basis, the role of CTO can be classified as follows:
- Developing and implementing a comprehensive technology strategy that aligns with business objectives by defining the roadmap and identifying trends.
- Researching and innovating technological solutions to align with market trends and technology adoption to improve business operations.
- Leading technology teams through the process of product development, implementation, and testing.
- Managing workforce development through hiring, mentoring, and ensuring effective teamwork.
- Ensuring reliability through product testing and compliance adherence while ensuring a high level of infrastructure availability.
- Developing a budget plan and managing resource allocation for various hardware, software, and workforce-related aspects to ensure cost-effectiveness.
- Developing and testing a disaster recovery and business continuity plan for potential security incidents or disasters.
- Managing the process of identification and mitigation of gaps and vulnerabilities – to ensure compliance with data privacy and security.
- Developing and implementing software development policies that are security-driven and incorporating security policies from the initial stages of development.
- Implementing and ensuring design-driven security of the product during the initial stages of development.
- Collaborating with business leaders, technology and security vendors, and other executives to clarify the organization’s requirements and guide strategic business decisions.
The role of the CTO has evolved, with a growing emphasis on balancing various responsibilities and adapting to shifting priorities. A Business Wire survey on what areas CTOs consider as their primary focus revealed that around 97.8% are involved in driving digital transformation, while 78.1% contribute to shaping business strategy. Additionally, 94.5% of CTOs also focus on revenue-oriented goals, and 87.7% oversee software development initiatives. These statistics reflect the multifaceted nature of the CTO role and the increasing need for a strategic, forward-thinking approach to technology leadership (Business Wire, 2021).
Key Skills Required for the Role
The role of chief technology officer requires a broad range of skills, which can be classified into technical, managerial, and interpersonal skills, as a CTO plays a key role in communications between various verticals across the organization (GeeksforGeeks, 2024).
Technical Expertise
A CTO must possess in-depth knowledge of various technologies, including software development, networking, cloud computing, data analytics, and security. As a result, extensive education in fields like IT, computer science, and business, along with certifications such as CCNA, CISSP, AWS, and CKA, are often required. Expertise in domains like data science, information technology, software development, cybersecurity, cloud computing, AI, and blockchain is also highly valued.
Leadership and Management
As a CTO in a leadership position, a proven track record of large-scale technology project development and management experience is a must. A CTO needs to have the ability to lead and motivate teams while building a strong work environment. Also, since the CTO serves as a crucial common point of connection between various teams and leaders, excellent communication and interpersonal skills are favorable for effective cooperation and workflow.
Business Acumen and Critical Thinking
With constantly changing business needs and technology landscape, a CTO must be agile and have the ability to think strategically, solve problems, and understand business principles, financial metrics, and market trends. This enables the organization’s technology infrastructure to adapt to emerging trends and changes.
Career Path for Aspiring CTOs
A Chief Technology Officer (CTO) is a professional with advanced technical expertise and proven experience in both technology and management domains. So, the journey to becoming a successful CTO requires continuous learning and skill development. The key steps to charting this career path can be outlined as follows:
Educational Foundation
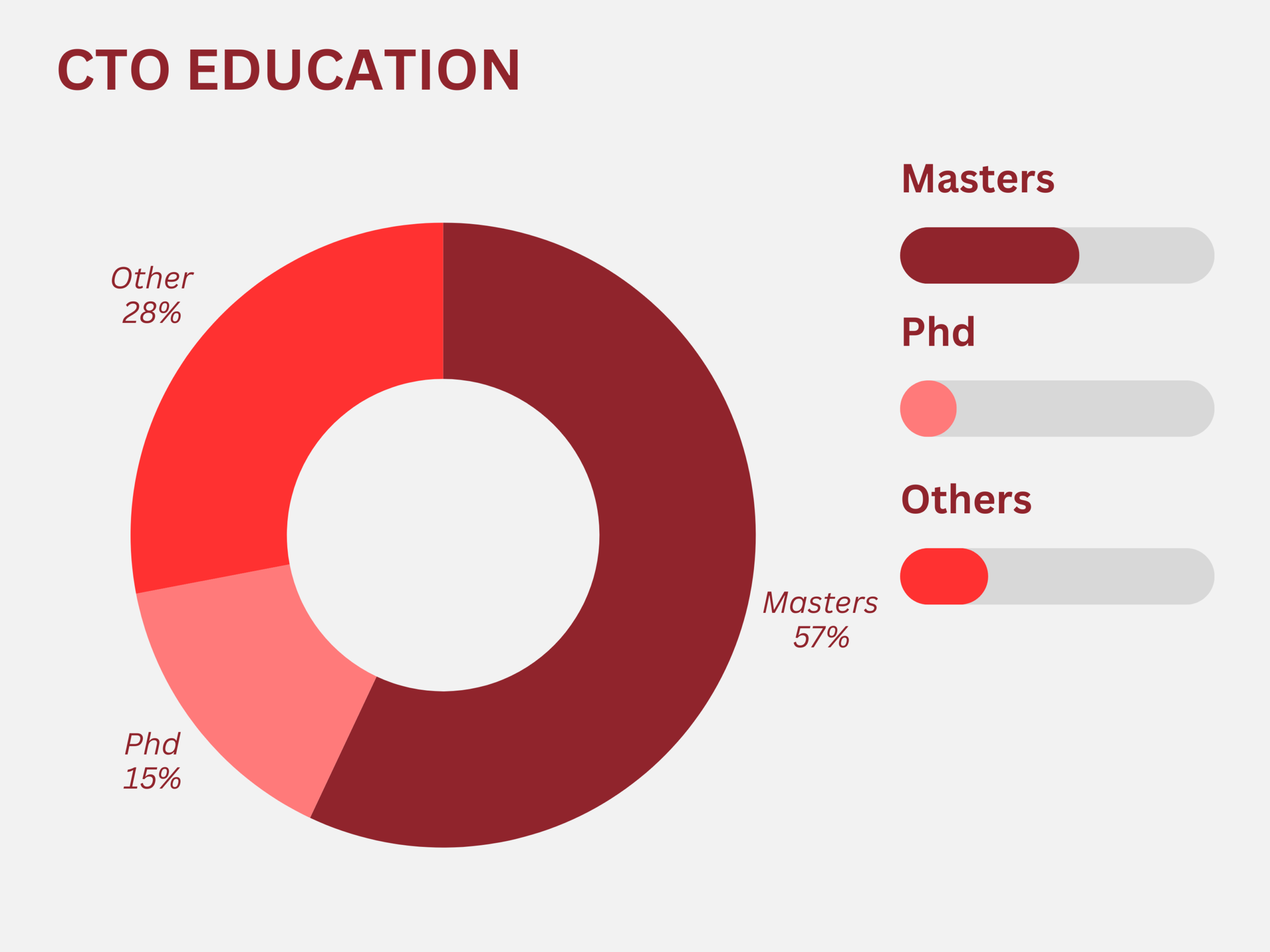
The journey begins with earning a degree in relevant fields such as computer science, information technology, or software engineering. Advanced degrees or additional education in business, finance, or economics can also be beneficial for acquiring management skills. A survey revealed that a substantial number of CTOs possess advanced degrees, with 57% holding a master’s degree and 15% earning a PhD. The findings also emphasize the high demand for specialized expertise, particularly in cybersecurity (76%), cloud computing (70%), and artificial intelligence (65%), highlighting the growing importance of these domains in the CTO role (STX Next, 2023).
Gaining Technical Expertise
Developing in-depth expertise in specialized areas of IT, such as cloud computing, data analytics, artificial intelligence, blockchain, or software development is critical. This can be achieved through work experience, certifications, online courses, and continuous learning.
Managerial Skills and Experience
Hands-on experience in both technical and managerial roles is essential. Leading teams, managing collaborations, and aligning technology initiatives with business requirements, allows a CTO to develop leadership skills and the ability to integrate technical capabilities with strategic objectives.
Building a Professional Network
Building connections with peers across the industry helps aspirants understand the current market and look for suitable job opportunities. Similarly, establishing connections with tech leaders and vendors builds business relationships, enabling the organization to grow the business.
“Transitioning from a technical leader to a CTO is a challenging but rewarding journey,” states Anuj Agarwal, CTO at NatWest. He explains, “It requires a shift from being a technology specialist to a technology leader… and a strategic thinker”. He further emphasizes, “While the technical skills that you bring from your role as a technical leader form a strong foundation, developing these additional skills and focusing on these areas will equip you to succeed as a CTO” (Agarwal, 2023).
Importance of Cybersecurity Management for CTOs
Developing and implementing robust IT security policies is a core responsibility of a CTO to protect the organization’s IT infrastructure. With the growing need for proactive security measures, the CTO must integrate security capabilities into the IT framework from the ground up. This involves close collaboration with cybersecurity experts to design and enforce policies that safeguard IT assets and ensure compliance with data privacy and digital security regulations. Key efforts include encryption, network security, threat detection, data protection, and incident response protocols.
A ransomware attack on Luxe Cart Inc. in March of 2023 revealed inadequate employee training on recognizing phishing emails. This points out the failure of higher management to implement a robust awareness training program. Thus underscoring the importance of the cybersecurity involvement of technology professionals and leaders (DigitalDefynd, 2025).
Regularly reviewing and updating security policies is vital for minimizing the organization’s risk exposure. As the CTO oversees software, IT development and management processes, their active involvement in cybersecurity ensures seamless integration and effective management of security measures. Towards security response, the role of a CTO can be classified into:
- Prioritization: This involves risk assessment, classification, scanning, threat intelligence, impact analysis, etc.
- Reaction: This involves responding to threats via incident detection, alerting, escalation, containment, and communication.
- Remediation: This involves finding the root cause, patching, updating, restoration, awareness, training, system hardening, etc.
Additionally, the role demands staying updated on emerging technological and cybersecurity trends to enhance the organization’s IT infrastructure and business operations while mitigating potential security threats.
Cybersecurity Management Essentials for Technical Professionals
In today’s rapidly evolving threat landscape, a CTO is responsible for integrating cybersecurity into IT and aligning these efforts with the organization’s broader business goals. Bridging the gap between technical expertise and business strategy requires a well-defined framework based on the following core principles:
- Align Security with the Organizational Mission: Ensure cybersecurity measures protect IT assets while maintaining an excellent user experience, aligning with the organization’s mission and goals.
- Adopt a Risk-Based Approach: Prioritize a risk-based approach to integrating cybersecurity with IT and addressing the most critical threats to business operations.
- Foster Cross-Department Collaboration: Encourage seamless collaboration among various departments to ensure a holistic and comprehensive implementation of cybersecurity measures.
- Effectively Communicate Cybersecurity Risks: Continuously communicate risks to non-technical stakeholders, emphasizing the business impact of threats to gain support and drive action.
- Utilize Metrics for Insights: Establish frameworks that provide metrics-based insights into IT and security performance, using them to deliver actionable recommendations for improving infrastructure to meet evolving business needs.
- Evaluate the ROI of Cybersecurity Initiatives: Assess the return on investment (ROI) of IT and cybersecurity projects to ensure optimal allocation of resources and value generation.
- Support Innovation and Digital Transformation: Drive innovation and digital transformation initiatives, ensuring security is a key enabler of business growth and operational efficiency.
- Promote a Security-First Culture: Embed cybersecurity into the organization’s culture by promoting employee training, awareness programs, and secure practices across all levels of the organization.
C|CISO: The Ultimate Cybersecurity Leadership Program
Cybersecurity is a critical component of technological development, making it essential for CTOs to prioritize it. According to studies, 51% of CTOs report spending most of their time on cybersecurity, and 48% of CTOs and equivalent roles directly report to cybersecurity heads (Shannon, 2024). Therefore, acquiring cybersecurity skills is likely to propel CTOs even further in their careers.
The Certified Chief Information Security Officer (C|CISO) program , developed by EC-Council, is designed for technology and cybersecurity professionals aspiring to excel in executive roles. It equips candidates with the leadership skills, technical expertise, and strategic knowledge necessary to manage and secure an organization’s information assets while aligning with business objectives.
Key Features of the C|CISO Program
- Comprehensive Curriculum: The program provides a deep dive into governance, risk management, incident response, and compliance, blending technical knowledge with business leadership principles.
- Cybersecurity Management for Leadership: C|CISO teaches professionals how to align cybersecurity strategies with business goals, adopt a risk-based approach, and drive decision-making at the executive level. It emphasizes effective communication with stakeholders, translating technical risks into business impact for informed decision-making.
- Building a Professional Network: Through C|CISO, participants gain access to a global community of top-tier cybersecurity professionals, fostering networking opportunities and peer collaboration.
- Showcasing Expertise: Achieving the C|CISO certification demonstrates advanced knowledge, experience, and leadership capabilities, making candidates stand out as trusted experts in the field.
As of January 2025, Indeed.com lists approximately 7,290 job openings for Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) (Indeed, n.d.), 216 of which require the C|CISO certification certification.
Reference
Agarwal, A. (2023, June 24). Moving from Tech Leader to CTO: My Journey and Lessons Learned. Freedium. https://freedium.cfd/https://anujxagarwal.medium.com/moving-from-tech-leader-to-cto-my-journey-and-lessons-learned-e059152e5b3b
Business Wire. (2021, September 16). Survey: CIO and CTO Responsibilities Converging, with Majority Now Influencing Business Strategy. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210916005629/en/Survey-CIO-and-CTO-Responsibilities-Converging-with-Majority-Now-Influencing-Business-Strategy
DigitalDefynd. (2025). 5 eCommerce Cybersecurity Case Studies [2025]. https://digitaldefynd.com/IQ/ecommerce-cybersecurity-case-studies/
GeeksforGeeks. (2024, October 07). How to Become a Chief Technology Officer. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/how-to-become-a-chief-technology-officer/
Indeed. (n.d.). Chief Information Security Officer Jobs. https://www.indeed.com/q-Chief-Information-Security-Officers-jobs.html?vjk=05657bdec185853b
LinkedIn. (n.d.). Hiring chief technology officers. https://business.linkedin.com/en-in/talent-solutions/resources/talent-acquisition/job-descriptions/chief-technology-officer
Shannon, K., G. (2024) Global Digital & Technology Officers Organization and Compensation Survey. Heidrick & Struggles. https://www.heidrick.com/-/media/heidrickcom/publications-and-reports/global-digital–technology-officers-report-2024.pdf
IDC. (2024, May 14). IT Skills Shortage Expected to Impact Nine out of Ten Organizations by 2026 with a Cost of $5.5 Trillion in Delays, Quality Issues and Revenue Loss, According to IDC. https://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS52128824
STX Next. (2023). The Global CTO Survey 2023 Report. https://www.thectosurvey.com/2023-report
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2024, December 17). Computer and Information Systems Managers. https://www.bls.gov/ooh/management/computer-and-information-systems-managers.htm
ZipRecruiter. (2025) Global chief technology officer jobs. https://www.ziprecruiter.com/Jobs/Global-Chief-Technology-Officer

